Monitoring your workspace's license and quotas
If you see Plans and not License in the left-hand menu, see this page.
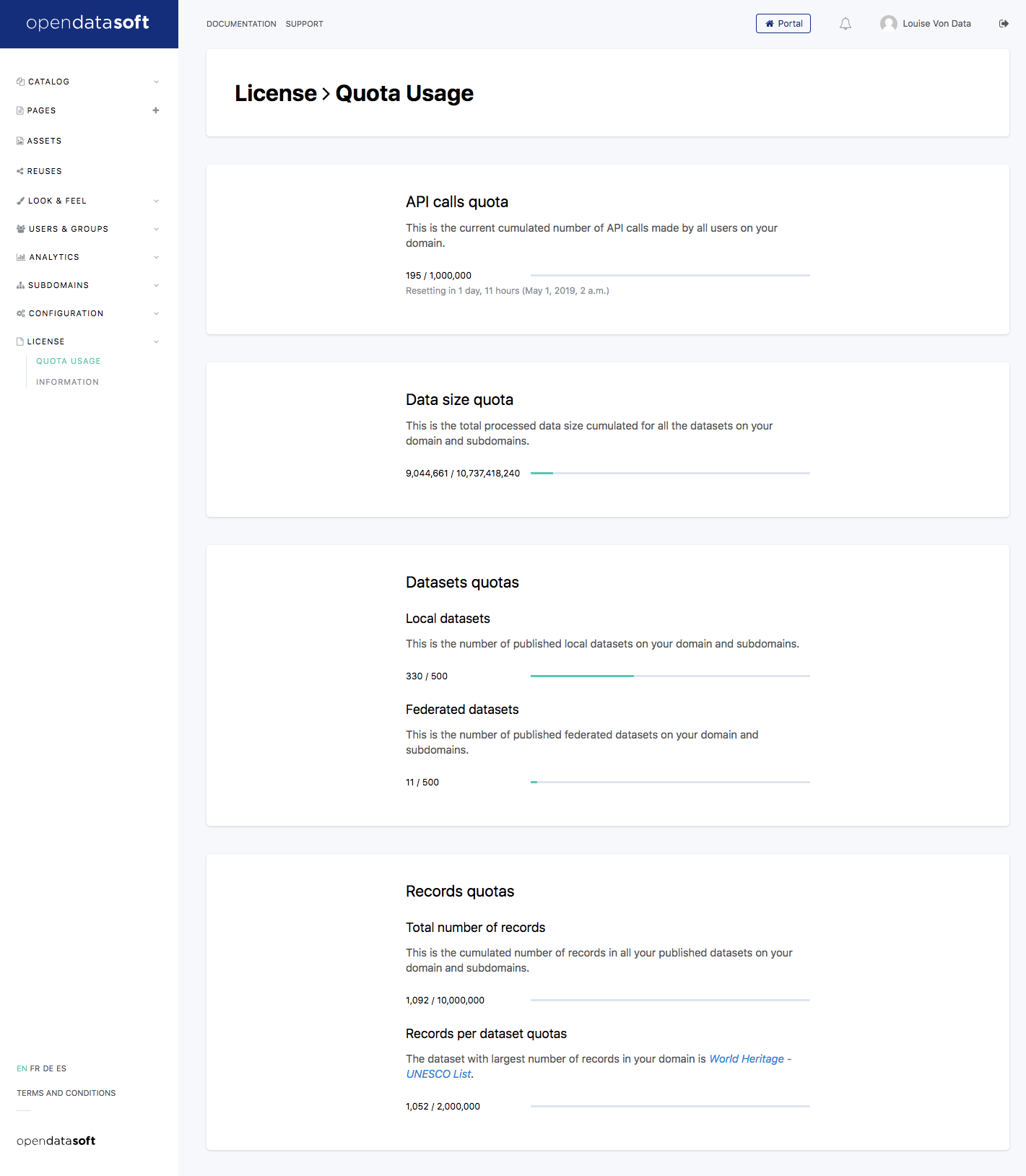
Go to the License > Quota Usage page.
This is the page where you can monitor your quota usage for the ongoing period.
You will find three usage indicators comparing the number of datasets, the number of records, and the number of API calls to the quotas defined in your license.
Your portal license
Before diving into which quotas exist on Opendatasoft portals, it is important to introduce the license topic. A license applies to each and every Opendatasoft portal. It is a contract between Opendatasoft and the portal owners, defining how much data can be injected into the portal and the consumption of this data.
For example, freemium portals can have up to five datasets, each having at most 20000 records.
Your license defines four global limits on your portal: the first one puts an upper limit on data consumption. The others regulate the amount of data you can inject into the portal.
API calls quota: Limits the number of requests made to the data within a given timeframe (usually within one month).
The number of API calls is a technical term, so it can be hard to understand, but it can be summarized like this: Every time someone accesses your portal, for example the datasets catalog page, the interface will make requests to the portal for the filter values, for the first page of 10 datasets, perhaps for a second page of 10 datasets, etc.. Each of these requests is an API call and counted within the quota.
API calls are made by visitors on your portal, but also by developers using the API to retrieve the data you published, as well as dashboards hosted outside of your portal.
Data size quota: Limits the total size of the data in datasets in the workspace.
Datasets quota: Constrains the total number of currently published datasets, for local datasets on the one hand, and for federated datasets on the other.
Records quota: Limits the total number of records within published datasets and also limits the maximum number of records per dataset.
You can see these quotas and check any information related to your license under the License section of the back office.
Setting default limitations on users
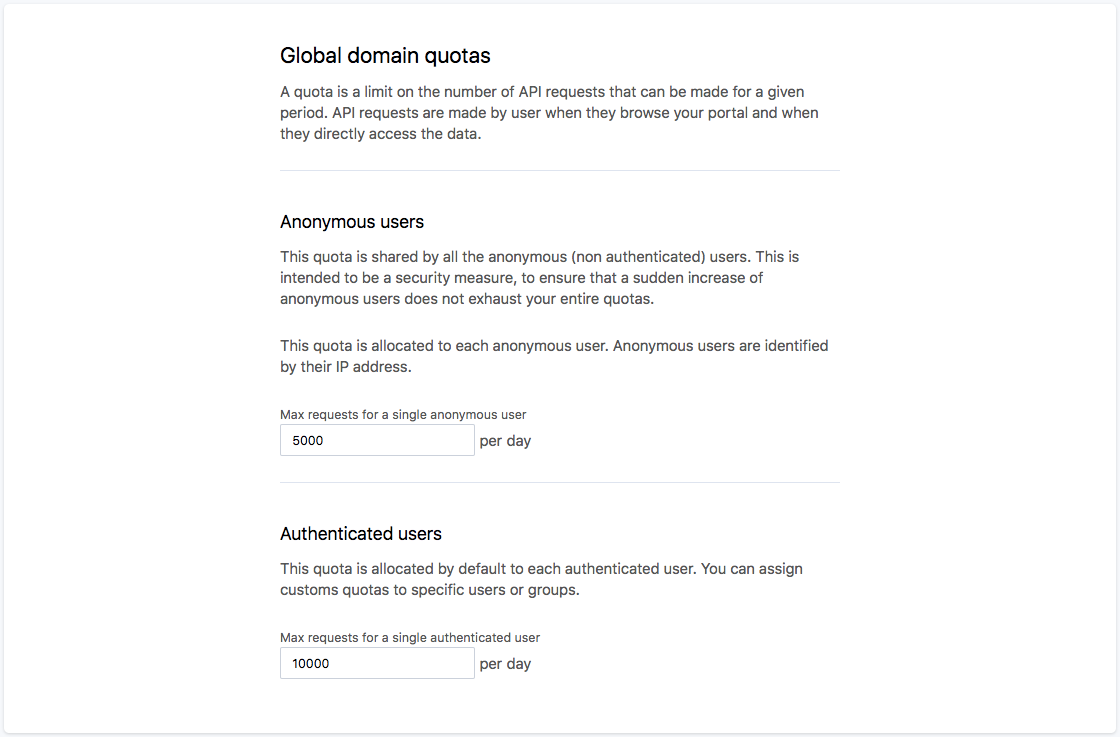
Since your portal has global upper limits set, you want to avoid having any one user use all of the license quota just by themself. You can therefore set general limits on users and, if your portal is open to anonymous users, set a different limit for them. You can also set a global limit for all anonymous users to be sure that they won't eat up all of your usage quota.
You'll be able to set these limits in the Security subsection of the Configuration section of your portal's back office.
When a user makes a request (be it an API call, a dataset creation of the publication of a dataset), we make sure they aren't running into the default limit set for them and isn't going over the global portal limit. Were this the case, a message would pop up to say so.
Setting specific limits for individual users and for groups of users
Some of your users have specific roles within your organization that justify their need for quotas larger than those given to them by default. For example, you may allow registered users to create only a few datasets each, but your Chief Data Officer will need to be able to publish as many datasets as your plan allows.
In order to do this, you'll have to go to the user's management page or their group management page to set a more appropriate limit for their use case.
Be aware that when you set new quotas for individual users or a group of users, the quota count starts back at zero for that period (even if they had previously reached their limit, and even if that limit was larger than the new limit).